Types Of Irregular Periods And What They Mean

With each menstrual cycle, the uterine lining (endometrium) prepares for foetal development. If fertilisation does not occur, the body excretes the endometrium during the cycle, which normally lasts three to eight days. While every woman’s menstrual cycle is different, it is abnormal when the periods are too light, too heavy, come too frequently, continue too long, are irregular, or occur after menopause.
Some reasons for irregular bleeding are insignificant. A variety of factors might cause the anomaly, and examples are hormone-based birth control, infection of the uterine lining or cervix, STI, blood coagulation issues, and other health conditions.
When do normal periods become abnormal? The four most prevalent types of atypical menstrual cycles are shown below.
- Polymenorrhea And Menorrhagia (Prolonged, Heavy Bleeding)
One of the most common types of menstrual bleeding is menorrhagia. Prolonged, severe bleeding is a symptom of the illness. In certain cases, the bleeding may interfere with routine everyday activities. This syndrome manifests itself in a variety of ways. Polymenorrhea (excessive menstruation), postmenopausal (menstrual periods after menopause), and metrorrhagia are the most common (bleeding between periods).
While there are other causes of menorrhagia, the following are the most common:
- Unbalanced hormones
- Fibroids in the uterus
- Miscarriage and other adverse pregnancy outcomes
- Inflammation of the cervix (PID)
- Infections or tumours in the pelvic cavity
- a bleeding or platelet problem
- Endothelin concentration is high.
- Dysmenorrhea (Excess Pain During Period)
Dysmenorrhea is a condition that causes pain and cramping during menstruation. Depending on the cause, the conditions might be classified as either primary or secondary. Primary dysmenorrhea is characterised by abnormal uterine contractions caused by a chemical imbalance. Secondary dysmenorrhea is frequently connected with underlying medical problems. The issue is more common in women who smoke, are fat, drink excessively during their periods, or begin menstruation at a young age. The following are the primary signs of this condition:
- Lower abdominal pain or cramping
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Leg and low back pain
- Vomiting
- Headaches
- Amenorrhea (Absent Periods)
Amenorrhea is a menstrual condition characterised by missing periods or missed for more than three cycles. This condition is classified into two types: primary amenorrhea and secondary amenorrhea. Menstruation does not begin at puberty in people who have primary amenorrhea. When a normal menstrual cycle becomes progressively irregular or missing, this is referred to as secondary amenorrhea.
Women can get this ailment for various causes, most of which are related to biological changes in their lives, such as breastfeeding, pregnancy, or menopause. It can also happen as a result of drugs or a medical condition, such as:
- Obesity
- Abnormal ovulation
- Consumption disorder
- Birth flaw
- Thyroid disease
- Excessive physical activity
- Menorrhagia (Extra Light Periods)
Menorrhagia is the inverse of hypomenorrhea, and hypomenorrhea is a condition marked by light periods. Menstruation usually lasts less than two days or is less than 80ml. The illness can be caused by hormonal contraceptives such as oral contraceptives or IUDs.
Other possible causes include:
- Body fat is low.
- Pregnancy
- Asherman’s syndrome, also known as intrauterine adhesions, is a condition in which there are adhesions between the uterus and the
- Stress or nervousness
- Unbalanced hormones
- Premature ovarian failure
If you have noticed any of the menstrual diseases listed above symptoms, consult an online lady doctor.


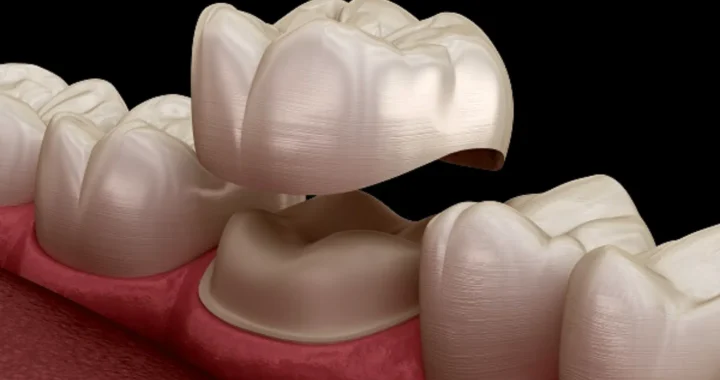 Dental Crowns –Restoring Strength, Function, And Aesthetics.
Dental Crowns –Restoring Strength, Function, And Aesthetics.  One-Person Wonder: Making Waves in the Massage Industry in Gunma
One-Person Wonder: Making Waves in the Massage Industry in Gunma  How Cataract Surgery in Nashville Improves Vision and Quality of Life
How Cataract Surgery in Nashville Improves Vision and Quality of Life  Maintaining Oral Health: The Role of Dentists in Richmond
Maintaining Oral Health: The Role of Dentists in Richmond 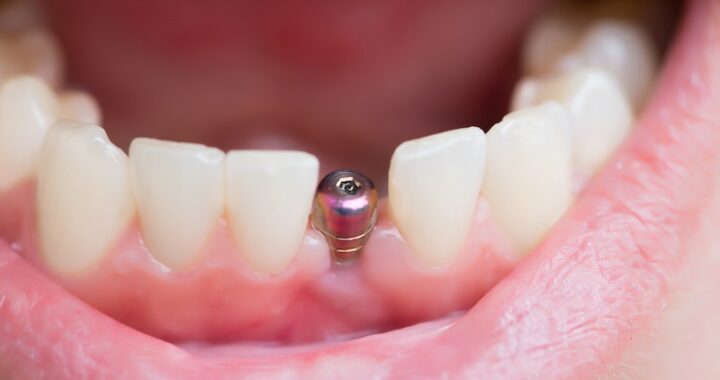 How to Choose the Best Implant Dentist in Sheffield: A Guide
How to Choose the Best Implant Dentist in Sheffield: A Guide 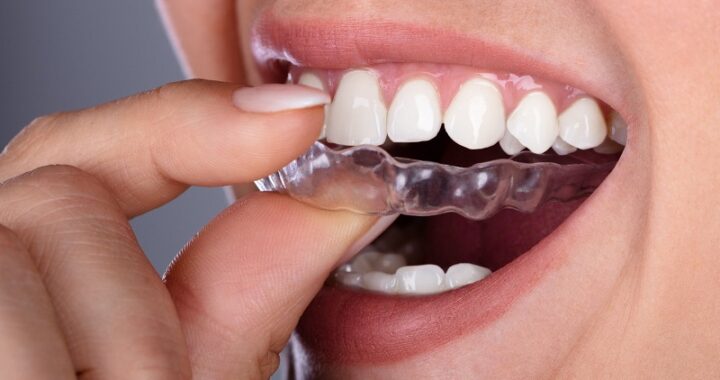 How Invisalign is Revolutionising Orthodontics in London
How Invisalign is Revolutionising Orthodontics in London 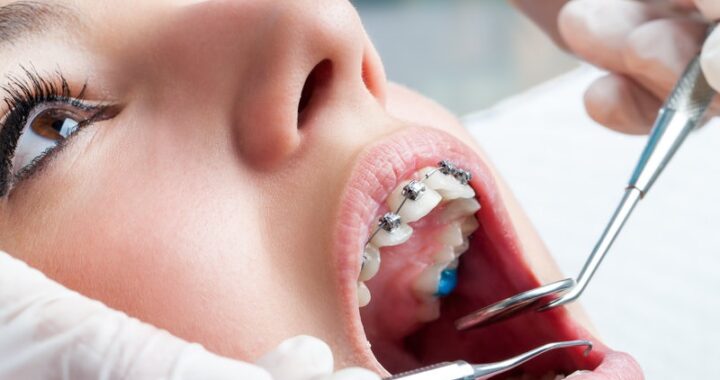 Veneers: A Popular Cosmetic Solution for a Beautiful Smile in London
Veneers: A Popular Cosmetic Solution for a Beautiful Smile in London