Orthognathic Surgery: All the Basics You Need to Know
Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery, is a type of surgical procedure that corrects a wide range of skeletal and dental irregularities. These irregularities can cause functional problems such as difficulty in chewing, breathing, and speaking, as well as aesthetic concerns such as facial asymmetry and a protruding jawline. Below are the basics of orthognathic surgery, including its benefits, types of procedures, and recovery process.
Benefits of Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery can provide a range of benefits to patients with severe skeletal and dental irregularities. Some of the benefits of orthognathic surgery include:
- Improved facial symmetry: Orthognathic surgery can correct facial asymmetry caused by skeletal irregularities.
- Improved breathing: Patients with obstructive sleep apnea or other breathing disorders can benefit from orthognathic surgery, which can help to improve airway function.
- Improved speech: Patients with speech disorders caused by skeletal irregularities can benefit from orthognathic surgery, which can improve articulation and pronunciation.
- Improved bite: Orthognathic surgery can correct a range of dental irregularities, including overbite, underbite, and crossbite.
- Improved oral health: Orthognathic surgery can improve oral health by correcting dental irregularities that can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues.
Types of Orthognathic Surgery
There are several types of orthognathic surgery, each of which is designed to address specific skeletal and dental irregularities. The most common types of orthognathic surgery include:
- Maxillary osteotomy: This procedure is designed to correct upper jaw irregularities such as overbite, underbite, and open bite.
- Mandibular osteotomy: This procedure is designed to correct lower jaw irregularities such as underbite and crossbite.
- Genioplasty: This procedure is designed to correct chin irregularities such as a protruding or receding chin.
- Combination procedures: In some cases, a combination of procedures may be necessary to correct complex skeletal and dental irregularities.
The Orthognathic Surgery Process
The orthognathic surgery process typically involves several steps, including:
Consultation
The first step in the orthognathic surgery process is a consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. During the consultation, the surgeon will evaluate your medical history, perform a physical examination, and take x-rays and photographs of your face and jaw.
Treatment Planning
Based on the results of the consultation, the surgeon will develop a treatment plan that addresses your specific skeletal and dental irregularities. This may involve a single procedure or a combination of procedures.
Pre-Surgical Preparation
Before the surgery, you will need to undergo several pre-surgical preparations, including orthodontic treatment to align your teeth, and nutritional counseling to ensure that you are healthy enough for surgery.
Surgery
The surgery itself typically takes several hours and is performed under general anesthesia. During the surgery, the surgeon will make incisions in your gums and jawbone and reposition the bones to correct the irregularities.
Recovery
The recovery process typically involves several weeks of rest and limited activity. You may need to wear braces or other dental appliances to maintain the position of your teeth and jaw during the healing process.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, orthognathic surgery carries some risks and complications, including:
Nerve damage: There is a risk of nerve damage during the surgery, which can cause numbness or tingling in the lips, tongue, or chin.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection following the surgery, which can lead to swelling, pain, and fever.
- Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding during and after the surgery, which may require additional treatment.
- Relapse: There is a risk that the bones may shift back to their original position after the surgery, which may require additional treatment.
- Difficulty with eating and speaking: Patients may experience difficulty with eating and speaking following the surgery, which can take several weeks to resolve.
It’s important to discuss the risks and potential complications with your surgeon before undergoing orthognathic surgery.
Conclusion
Orthognathic surgery can be a life-changing procedure for patients with severe skeletal and dental irregularities. The procedure can improve facial symmetry, breathing, speech, bite, and oral health.
There are several types of orthognathic surgery, including maxillary osteotomy, mandibular osteotomy, genioplasty, and combination procedures. The orthognathic surgery process typically involves several steps, including consultation, treatment planning, pre-surgical preparation, surgery, and recovery.
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications associated with orthognathic surgery, which should be discussed with your surgeon before undergoing the procedure.


 Innovations in Health Screenings: Exploring the Latest Technologies in Clinic Services
Innovations in Health Screenings: Exploring the Latest Technologies in Clinic Services 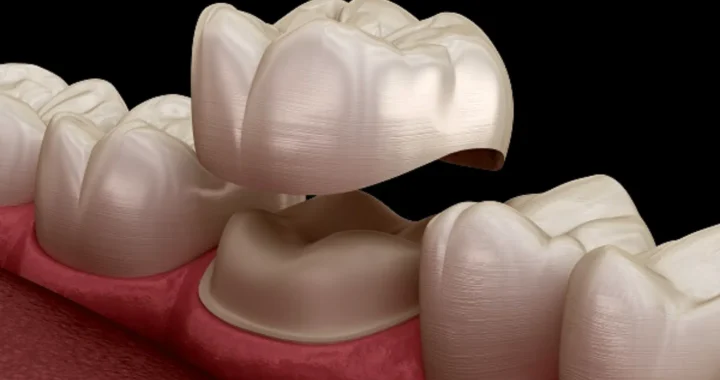 Dental Crowns –Restoring Strength, Function, And Aesthetics.
Dental Crowns –Restoring Strength, Function, And Aesthetics.  One-Person Wonder: Making Waves in the Massage Industry in Gunma
One-Person Wonder: Making Waves in the Massage Industry in Gunma  How Cataract Surgery in Nashville Improves Vision and Quality of Life
How Cataract Surgery in Nashville Improves Vision and Quality of Life  Maintaining Oral Health: The Role of Dentists in Richmond
Maintaining Oral Health: The Role of Dentists in Richmond 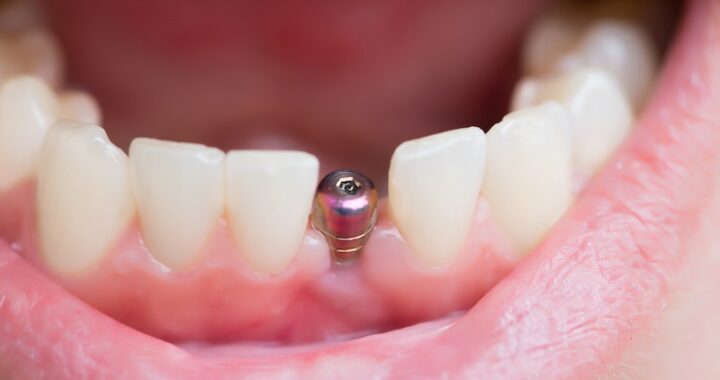 How to Choose the Best Implant Dentist in Sheffield: A Guide
How to Choose the Best Implant Dentist in Sheffield: A Guide